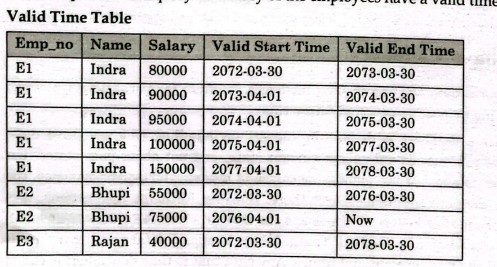
Explain the following terms: a) Extent b)Temporal database c) Degree of homogeneity of DBMS

Extent Ans: An extent is a logical unit of database storage space allocation made up of a number of contiguous data blocks. One or more extents in turn make up a segment. When the existing space in a segment is completely used, Oracle allocates a new extent for the segment. When Extents Are Allocated When you create a table, Oracle allocates to the table's data segment an initial extent of a specified number of data blocks. Although no rows have been inserted yet, the Oracle data blocks that correspond to the initial extent are reserved for that table's rows. If the data blocks of a segment's initial extent become full and more space is required to hold new data, Oracle automatically allocates an incremental extent for that segment. An incremental extent is a subsequent extent of the same or greater size than the previously allocated extent in that segment. For maintenance purposes, the header block of each segment contains a directory of the extents in that segment. Tempo
.png)







.gif)
.gif)




