Explain the storage mechanisms of HBase. Differentiate HBase with RDBMS.
STORAGE MECHANISM IN HBASE
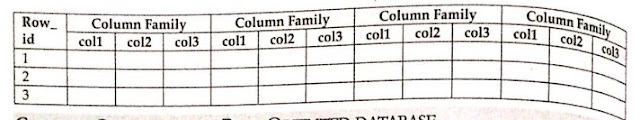
HBase is a column-oriented database, with tables ordered by row. Only column families, which are key-value pairs, are defined in the table structure. A table contains many columns families, each of which can include any number of columns. Subsequent column values are saved on the disk in a logical order. A timestamp is associated with each cell value in the table.
In a nutshell, in an HBase:
- The table is a collection of rows.
- The row is a collection of column families.
- A Column family is a collection of columns.
- The column is a collection of key-value pairs.
An example schema of a table in HBase is provided below.
Difference between HBase and RDBMS.
HBase
- HBase is schema-less, it does not have the concept of fixed columns schema; defines only column families.
- It is built for wide tables. HBase is horizontally scalable.
- No transactions are there in HBase.
- It has de-normalized data.
- It is good for semi-structured as well as structured data.
RDBMS
- An RDBMS is governed by its schema, which describes the whole structure of tables.
- It is thin and built for small tables. Hard to scale.
- RDBMS is transactional.
- It will have normalized data.
- It is good for structured data.



Comments
Post a Comment