Explain API Controllers.
API Controllers
- API Controller is just a normal Controller, that allows data in the model to be retrieved or modified, and then delivered it to the client. It does this without having to use the actions provided by the regular controllers.
- The data delivery is done by following a pattern known by name as REST. REST Stands for REpresentational State Transfer pattern, which contains 2 things:
b) URLs that define operational tasks. These operations can be sending full or part of data, adding, deleting, or updating records. In fact, it can be anything.
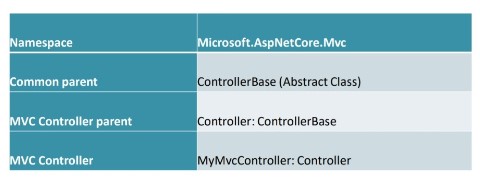
- MVC and API controllers both derive from the Controller class, which derives from ControllerBase:
public class MyMvc20Controller Controller {} [Route("api/ [controller]")]
public class MyApi20Controller Controller {}
- As of Core 2.1 (and 2.2), the template-generated classes look a little. different, where a Web controller is a child of the Controller class and an
- API controller is a child of ControllerBase.
public class MyMvc21Controller: Controller {}
[Route("api/[controller]")]
public class MyApi21Controller : ControllerBase {}
This can be expressed in the table below:



Comments
Post a Comment