Explain Virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI).
Virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI)
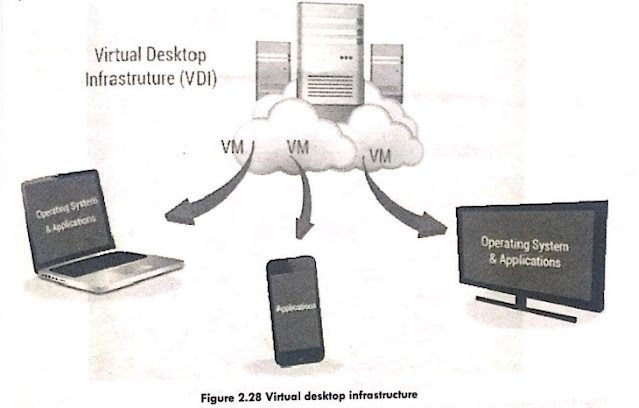
Virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) is a data center virtualization technique that runs a desktop operating system on a centralized server. VDI is a variant of the client-server computing technology, sometimes known as server-based computing. VMware originated the phrase. VDI is divided into two approaches: persistent and nonpersistent. Persistent VDI gives each user his or her desktop image, which may be altered and stored for future use in the same way that a typical physical desktop can. Nonpersistent VDI creates a pool of consistent desktops that users can access as required. When a user logs out, nonpersistent desktops revert to their previous state.
Benefits
- Cost efficiency
- Instant backup capabilities Reduced lag time
- Added security features
- Simplified management
- Fewer compatibility issues
Best virtual desktop infrastructure applications
Amazon WorkSpaces, IBM Cloud, Cisco VXI, VMware Horizon Cloud, Red Hat Virtualization, Citrix Virtual Apps & Desktops, SolarWinds Virtualization Manager, etc.
.gif)



Comments
Post a Comment