Difference between traditional computing and virtual environment.
TRADITIONAL AND VIRTUAL ENVIRONMENT
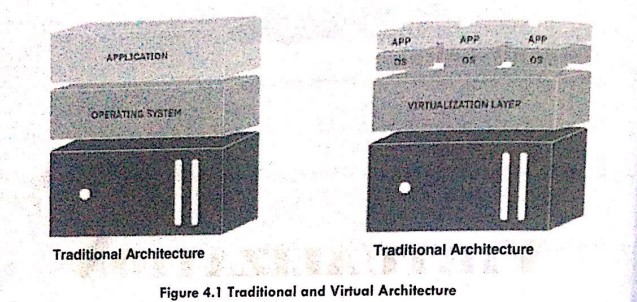
In a typical physical computing environment, software like an operating system (OS) application has direct access to the underlying computer hardware and components, such as the memory, storage, specific chipsets, and OS driver versions. This caused significant problems with progress setup and made it impossible to relocate or reinstall the software on new restoring backups after a breakdown or disaster. Virtualization involves the installation of a Hyper-V which acts as an intermediary between the program and the underlying hardware. Once a hypervisor is installed, the software uses virtual representations of computer components, such as virtual processes rather than actual processors.
Virtualized computing resources are supplied as separate instances known as Virtual Machines (VM into which operating systems and applications can be loaded. Virtualized systems may host numerous VMs at the same time, but each VM is logically separated from the others. This implies that a malwa attack or a VM crash will not impact the other VMs. Support for numerous VMs significantly improves system usage and efficiency. Instead of purchasing ten different servers to host ten physical applications, the single virtualized server might support the same ten applications deployed on ten virtual machines on the same system. This increased hardware utilization is a significant benefit of virtualization, as it provides great potential for system consolidation, decreasing the number of servers and power consumption of business data centers.



Comments
Post a Comment