Explain Web Services and APIs.
Web Services and APIs
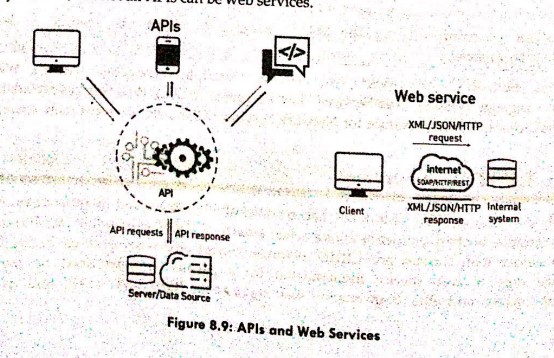
Web services and APIs can be frequently mistaken for one another. Most online services include an API, which is used to get data using a set of commands and functions. Web services and APIs are accessed through HTTP/HTTPS to enable communication between service providers and customers and they both call a function, process data, and receive a response. API is a lightweight architecture that is suitable for devices with low bandwidth such as smartphones and as SOAP is required to send and receive network data, web services are not lightweight. APIs can use any form of communication, but a Web service only uses SOAP, REST, and XML-RPC. APIs support URL, request/response headers, caching, and versioning content formats however web services only support HTTP. One important thing to consider is that all web services may be APIs, but not all APIs can be web services.
For instance, Twitter provides an API that allows developers to read tweets from a server and gather data in JSON format.



Comments
Post a Comment