Write short notes: a. GFS and HDFS b. Google Cloud Datastore c. Multi-tenant cloud
a)Google File System (GFS)
- The Google File System is a scalable distributed file system designed for big data-intensive distributed Applications. It offers fault tolerance while running on low-cost commodity hardware and gives great distributed file systems, its design has been influenced by observations of application workloads and the aggregate performance of a large number of customers. While GFS has many of the same aims as past technical environments, both current and prospective, which represent a significant divergence from Certain preceding file system assumptions. As a result, established options have been reexamined, and Grammatically alternative design points have been explored.
- Google File System (GFS) is a scalable distributed file system (DFS) designed by Google Inc. to meet Google's growing data processing needs. GFS supports huge networks and linked nodes with fault tolerance, dependability, scalability, availability, and performance. GFS is comprised of storage systems constructed from low-cost commodity hardware components. It is designed to meet Google's various data consumption and storage requirements, such as their search engine, which creates massive volumes of data that must be kept. The Google File System took advantage of the strengths of off-the-shelf servers while reducing hardware flaws. GoogleFS is another name for GFS.
- The storage requirements were satisfied satisfactorily by the file system. It is widely utilized within Google as a storage platform for the collection and processing of data utilized by our services as well as research and development projects requiring big data sets. The biggest cluster to date has hundreds of terabytes of storage spread across thousands of disks on over a thousand servers, and it is used concurrently by hundreds of clients.
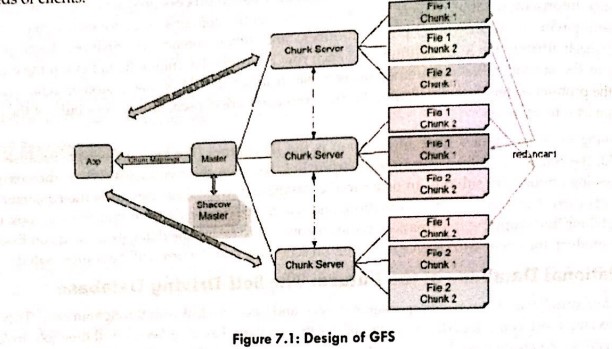
- The GFS node cluster consists of a single master and numerous chunk servers that are constantly accessed by various client systems. Data is stored on local drives by chunk servers as Linux files. Data is stored in big chunks (64 MB), which are duplicated at least three times on the network. Because of the huge chunk size, network overhead is reduced.
- GFS is intended to meet Google's huge cluster requirements without burdening apps. Pathnames are used to identify files in hierarchical folders. The master controls metadata such as namespace, access control data, and mapping information by interacting with and monitoring the status updates of each chunk server via scheduled heartbeat messages.
GFS Features Include
- Fault tolerance
- Critical data replication
- Automatic and efficient data recovery High aggregate throughput
- Reduced client and master interaction because of large chunk server size
- Namespace management and locking
- High availability
b)GOOGLE CLOUD DATASTORE
Google Cloud Datastore is a Google Cloud Platform service that provides a highly scalable, fully managed NoSQL database. Cloud Datastore is based on Bigtable and Megastore technologies from Google. Cloud Datastore is a NoSQL document database designed for online and mobile applications that require automated scalability, excellent performance, and simplicity of development.
Features of Google Cloud Datastore include:
Atomic transactions.
Cloud Datastore can perform a series of operations in which they succeed.
High availability of reads and writes.
Cloud Datastore is hosted in Google data centers, which employ redundancy to reduce the effects of single points of failure.
Massive scalability with high performance.
To manage scalability automatically, Cloud Datastore has a distributed design. Cloud Datastore employs a combination of indexes and query limitations to ensure that your queries grow with the size of your result set rather than the size of your data set.
Flexible storage and querying of data.
Cloud Datastore is easily mapped to object-oriented and scripting languages, and it is accessible to applications via a variety of clients. It also has a query language that is similar to SQL.
Balance of strong and eventual consistency.
Cloud Datastore assures that entity lookups using key and ancestor searches always provide highly consistent results. All other searches become consistent in the end. The consistency models enable your application to provide an excellent user experience even when dealing with massive volumes of data and users.
Encryption at rest.
Cloud Datastore automatically encrypts all data before it is written to disk and immediately decrypts the data when accessed by an authorized user. For further information, see Server-Side Encryption.
Fully managed with no planned downtime.
Google manages the Cloud Datastore service, allowing you to focus on your application. When the service is scheduled for an upgrade, your application can continue to use Cloud Datastore.
c)MULTI-TENANT CLOUD
A multi-tenant cloud is a cloud computing architecture that enables clients to share computer resources in either the public or private cloud. Each tenant's data is segregated and hidden from other residents. Users in a multi-tenant cloud system have their area to store their projects and data. Each segment of a multi Tenant cloud network comprises sophisticated permissions to provide each user access to just their stored formation while also protecting them from other cloud tenants. Each tenant's data is unavailable to all her tenants inside the cloud architecture and may only be accessed with the cloud provider's rights.
Customers, or tenants, in a private cloud, might be various individuals or groups inside a single firm, but on a public cloud, completely separate enterprises can securely share their server space. The multi-tenancy approach is used by the majority of public cloud providers. It enables them to run servers with single lances, which saves money and streamlines upgrades.
BENEFITS OF MULTI-TENANT CLOUD
Multi-tenant cloud networks offer more storage and better access than single-tenancy clouds, which have restricted access and security settings. Cloud computing multi-tenancy makes a bigger pool of resources available to a bigger number of individuals without losing privacy or security or slowing down applications. The virtualization of storage locations in cloud computing enables flexibility and simplicity of access from virtually any device or location.
Example of Multi-tenancy
The structure of multi-tenant clouds can be compared to that of an apartment building. Each tenant has access to their apartment within the framework of the building's agreement, and only authorized persons are permitted to enter the specified apartments. However, utilities such as water, power, and common rooms are shared by the entire building.



Comments
Post a Comment