Explain about concept hierarchy with example.
Concept Hierarchies
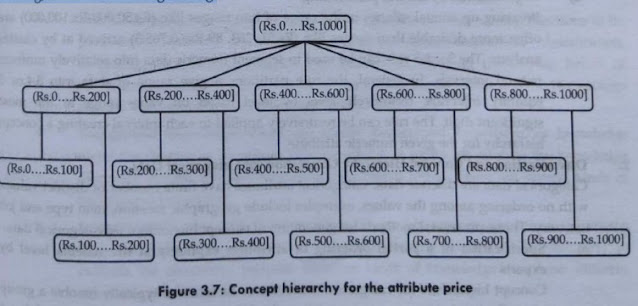
A concept hierarchy for a given numeric attribute defines a discretization of the attribute. Concept hierarchies can be used to reduce the data collecting and replace low-level concepts (such as numeric value for the attribute age) with higher-level concepts (such as young, middle-aged, or senior) Although detail is lost by such generalization, it becomes meaningful and it is easier to interpret. In the multidimensional model, data are organized into multiple dimensions, and each dimension contains multiple levels of abstraction defined by concept hierarchies. This organization provides users with the flexibility to view data from different perspectives. Data mining on a reduced data set means fewer input/output operations and is more efficient than mining on a larger data set. Because of these benefits, discretization techniques and concept hierarchies are typically applied before data mining, rather than during mining.



Comments
Post a Comment