Explain JSP access model with suitable diagram.
JSP Access Model
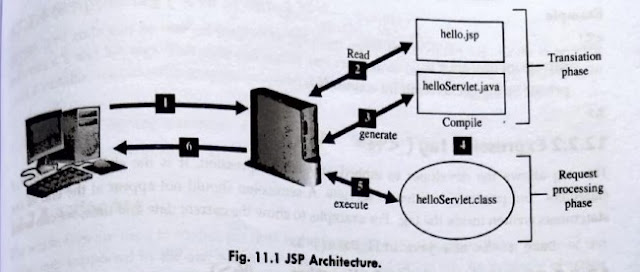
When a user goes to a website that is developed by using JSP and tries to access the JSP page by using a web browser, the following steps are performed to process the request and return the result to the user:
1. User sends JSP request to the Web server through a web browser to the webserver with JSP engine.
2. The Web server recognizes that the file required is a JSP file, therefore passing the JSP file to the JSP Engine.
3. If the JSP file has been called the first time, the JSP file is parsed, otherwise, go to step 5. The JSP engine generates a special servlet file from the JSP file.
4. The servlet file is compiled into an executable class file. JSP engine then forwards the original request to a servlet engine and the servlet is instantiated.
5. The servlet engine loads the servlet class and executes it by calling init and service methods. During execution, the servlet produces an output in HTML format, which is passed to an HTTP response.
6. The web server forwards the HTTP response to the browser in terms of static HTML content. Finally, web browser handles the dynamically generated HTML page HTTP response and results are displayed on the web browser. inside the
Typically, the JSP engine checks to see whether a servlet for a JSP file already exists and whether the modification date on the JSP is older than the servlet? If the JSP is older than its generated servlet, the JSP container assumes that the JSP hasn't changed and that servlet file is not generated. This makes the process more efficient than with other scripting languages (such as PHP) and therefore faster.



Comments
Post a Comment