Explain cloud adoption and rudiments.
Cloud Adoption
- Here Cloud Means The environment of the cloud where the cloud services are being operated.
- Adoption term states that accepting the services of new technology. Adoption means following some kind of new trend or existing trend or technology.
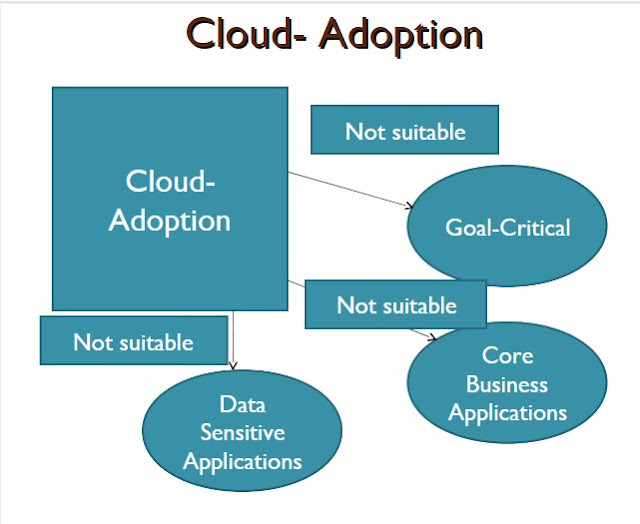
- This Cloud adoption is suitable for low-priority business applications. Because as we have already discussed that cloud computing is not beneficial for long-term projects. It supports some interactive applications that combine two or more data sources.
- These applications must have low availability requirements and short life spans. For example:-if a marketing company requires to grow its business in the whole country in a short span of time then it must need a quick promotion or short promotion across the country.
- Cloud Adoption is useful when recovery management and backup recovery-based implementations are required. By considering t e above key points we conclude that it is only suitable for applications that are modular and loosely coupled.
- It will work well with research and development projects. It means the testing of new services, design models, and also the applications that can be get adjusted on small servers.
- Applications that requires different level of infrastructure throughout the day or throughout the month should be deployed Through the cloud. The applications whose demand is unknown can also be deployed using clouds.
Cloud-Rudiment
- In this Topic, we will discuss the Essentials or rudiments of cloud computing.
- Here the higher-level capabilities of the cloud are as follows:-
- Resource Aggregation and integration
- Resource Aggregation and integration
Cloud solution Integrates or aggregates the information of These 3 resources which are shown in the fig of the previous slide. After That, the integrated information will be sent into a central logical view. - Application Services
Here app services state that the services are related to a particular s/w. The Application instances represent the agreement between the service provider and the consumer to use services on an On-Demand basis. Cloud also provides the facility of reservation of resources. It means that it is guaranteed that at a given point in time the resources or the services will surely be available for the consumer - Self-Service portal
An ex of self-service r Self-service is a facility provided by the cloud to consumers. This supports the account owners signing up and being able to use the purchased capacity. Users can request machine or entire multi-machine environments and monitor and control them using a web-based self-service portal. In restaurants, I need one glass of water But there is nobody to serve Customer will go itself and take a glass of water - Allocation Engine
The DRM provides the automated allocation and reallocations of resources. The DRM is a key component of any cloud solution that maximizes the efficiency of the IAAS. The DRM is Dynamic resource management. - Reporting and accounting
The actual resource allocation and the actual cloud usage will be get recorded or collected in an accounting database. The data will be available centrally to create reports of usage. For example:-capacity allocated vs. capacity used by the consumer
We have discussed earlier that this is a self-service portal provided by the cloud.
- Self-service
We have discussed earlier that this is a self-service portal provided by the cloud.- Dynamic Workload management
Here Cloud virtual machines are enabled with automated s/ws that control the workflow requests. Also, virtual machines are enabled with a lifecycle that increases the effective utilization of resources. - Resource Automation
It clearly shows that the resources will automatically plus effectively utilized As and when they are required by the service consumers. - Metering of resources
The help of the metering of resources in any cloud user organization would bring transparency to the business and environment for the management to see the usage of resources.OR,
Cloud Adoption
- Cloud Adoption is a strategic move by organizations of reducing cost, mitigate risk, and achieving scalability of database capabilities. Cloud adoption may be up to various degrees in an organization, depending on the depth of adoption. In fact, the depth of adoption yields insight into the maturity of best practices, and enterprise-ready cloud services availability.
- Organizations that go ahead with the strategic decision of adopting cloud-based technologies have to identify potential security thefts and controls, required to keep the data and applications in the cloud secure. Hence there is a need for compliance assessment during cloud adoption.
The following measures are taken for compliance assessment to ensure the security and accountability of data and applications in the cloud services:
- Matching the security requirements of the organization with the security capabilities of the cloud service provider
- Analyzing the security policies of the cloud service provider along with a history of transparency and security-related practices
- Proper understanding of the technical aspects of data and traffic flow
- Proper understanding and documentation of the roles and responsibilities of the cloud service provider
- Understanding of the certifications and compliances that can be leveraged from the cloud service provider




Comments
Post a Comment