Explain Single Sign-On (SSO) and Federated Identity Management (FIDM).
Single Sign-On (SSO)
An authentication procedure in a client/server connection in which the user, or client, enters one name and password and has access to several applications or resources inside a business. When going from one application to another, 'Single Sign On' eliminates the need for the user to enter additional authentications. Companies increasingly utilize Single Sign-On software to overcome the problem of utilizing the separate username and password combinations for multiple servers. This software allows the user to log in only once and control access to other systems. As indicated in the picture below, SSO uses a single authentication server to manage numerous accesses to other services.
The following steps describe how Single Sign-On software works:
- The user logs into the authentication server using a username and password.
- The authentication server returns the user's ticket. The user sends the ticket to the intranet server.
- The intranet server sends the ticket to the authentication server.
- The authentication server sends the user's security credentials for that server back to the intranet server.
- If an employee quits the organization, deactivating the user account at the authentication server prevents the person from accessing any of the firm's systems.
FEDERATED IDENTITY MANAGEMENT (FIDM)
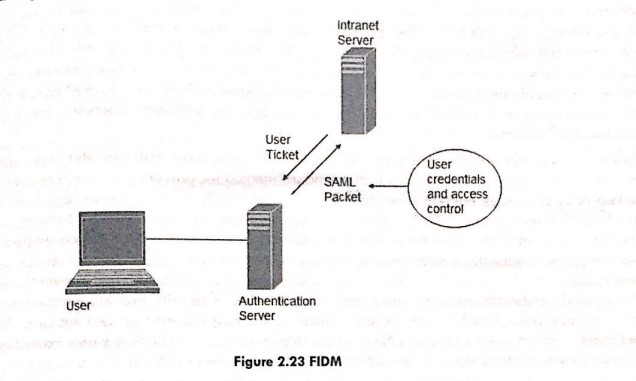
The term FIDM refers to the technologies and protocols that allow a user to package security credentials across security domains. It uses Security Markup Language (SAML) to bundle a user's security credentials, as seen in the figure below:





Comments
Post a Comment